RetroLisa
--------- | 1990s Internet &
World Wide Web | |
|
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________
|
|
|
RetroLisa
| ___________________________________________________________________ | __ | _____________________________ | _______ | Going Online
In the 1990s, there were several ways for a computer user to go online.
the internet
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks. In the 1970s and 1980s, access was limited to computers that were part of a university or government network. Casual computer users first gained access in 1989.
internet features in the 1990s
independent online systems
- Bulletin board systems were electronic message boards for PC users. Early boards were accessed by dialing directly to the host computer. In the 1990s, many boards moved to the Internet, where they could be accessed with the Telnet feature. A typical BBS also offered e-mail, chat rooms, games and file downloading. The first chat abbreviations and emoticons were used here. BBS traffic reached its peak in 1996.
- Usenet was a network of servers that allowed participants to download files and post messages to newsgroups. The servers were originally accessed by dialing into a Unix network. In the 1990s, many servers could also be accessed through an online service or over the Internet. Usenet was the birthplace of FAQ (frequently asked questions), and in 1994 it was the site of the first major spam incident.
- Electronic information services provided subscribers with access to financial reports, newspaper articles, shopping sites and academic databases. Users could dial into the services directly or access them from a public data network. In addition to the subscription fees, each service charged various online fees and royalty fees. Information services and public data networks were not considered part of the Internet.
- E-mail services made it possible for businesses, organizations and computer hobbyists to create e-mail accounts on a subscription basis. Popular e-mail services in the 1990s included MCI Mail, Easylink, AT&T Mail and Sprintmail.
- Online services were dial-up information networks for computer hobbyists. In the 1990s, online services provided e-mail, chat rooms, instant messaging, forums, shopping, databases and games for their members. In 1995, the most popular online services were America Online, CompuServe, Genie, Delphi, Prodigy and the MSN Network.
| |
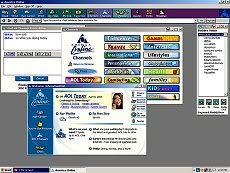
America Online

AOL Sounds
Usenet Tutorial
MCI Mail
Prodigy
CompuServe
The BBS Corner
Hobbes' Internet Timeline
|
coming together
At first, each online system operated independently from the others. This began to change in the 1980s, when gateways made it possible for some systems to interact with each other. In 1980 and 1985, ARPANET and BBS members gained access to Usenet servers. In the mid 1990s, subscribers of America Online, CompuServe, Prodigy and EarthLink could also post on Usenet. Beginning in 1986, a handful of e-mail services established connections between their networks.
Everything came together in the 1990s. After the Internet was made available to the general public, it became the backbone to which all other systems were connected. Many bulletin board systems, Usenet servers and databases moved their operations to the Internet at this time. Internet access for everyone became a reality when the subscription-based online services were first permitted to connect to the Internet. The scene was set for the online explosion that we know today.
| |
|
_________________________________________
|
|
|
RetroLisa
| _______________________________________________________________________________ | __ | _________________ | _______ | The World Wide Web
the internet vs. the web
Today, the terms Internet and World Wide Web are used to describe the same thing: using your computer and a service provider to go online and access a seemingly endless number of web pages and websites.
It's easy to forget that the Web and the Internet are actually two different things. The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks. The Web is a service that travels over the Internet.
web basics
The World Wide Web is an intricate collection of digital documents residing on the Internet. The documents are linked to each other via hypertext technology. Users gain access to these documents by installing standard software programs known as browsers.
In a traditional network, the actual computers are linked. On the Web, the whole procedure is simplified because only the documents are linked. This makes navigating the online world easier for the average computer user.
Documents and activities are web-based if they use a web browser. Off-web activities require separate programs such as RealPlayer, Adobe Reader, Telnet or Outlook. Many websites provide links to off-web content.
The Web was launched in 1991 with one web server and four web pages. It quickly became very popular, creating the Internet revolution that we know today.
Archived Copy Of The First Web Page
web browsers
The first web browser was known as WorldWideWeb. It was introduced in 1990 and was developed by Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the Web concept. In 1992, Midas, Erwise and Viola were browsers written for Unix computers. Lynx was a text-only browser also introduced in 1992.
The web pages in existence at the time contained a small amount of graphics, which could only be seen by computers that were compatible with the browsers. In 1993, the new Mosaic browser made the graphics viewable to everyone, and the use of images on web pages began to increase.
MacWWW, MacWeb and MacLynx were text-only browsers written for MacIntosh computers. IBrowse was released for Amiga computers in 1996.
Netscape Navigator was introduced in 1994, and Opera and Internet Explorer were introduced in 1995.
WorldWideWeb Browser
Web Browser History
Viola
Netscape Navigator
MacWeb
| |
|
_________________________________________
|
|
|
RetroLisa
| _______________________________________________________________________________ | __ | _________________ | _______ | Internet Access
Access to the online world is provided by companies known as internet service providers. The industry was born in 1989 when a handful of online services and commercial providers were first permitted to connect to the Internet.
After 1992, the term Internet access referred to both the traditional Internet and the Web.
dial-up
Dial-up technology was introduced for personal computers in 1977. This created an exciting new world full of bulletin board systems and online services, all accessible with a simple phone line and modem. In 1989, it became possible to use a BBS or online service to connect to the Internet. CompuServe was the first traditional online service to offer Internet access.
In 1989, The World was the first new company to specialize in Internet access.
In 1992, the service providers began to add Web access to their regular Internet offerings. Delphi was the first, followed by Prodigy, CompuServe, MSN Network and America Online in 1995.
More providers joined the ranks of ISPs in the mid 1990s. They included AT&T Worldnet, Mindspring and EarthLink. In the late 1990s, Netzero, Juno and Bluelight offered the first free dial-up access.
Beginning in 1996, a service known as WebTV used a standard TV and set-top box to provide Web access to people who didn't want the hassle or expense of buying a computer.
WebTV
EarthLink
The World
broadband
High-speed access was first made available to the public in 1996. This technology transmits Internet signals through phone and cable lines at speeds considerably higher than dial-up. Pages load almost instantly, the connections are always available, and the phone lines remain open for telephone use. In 1996, Rogers Communications in Canada was the first high-speed provider. Other high-speed services in the late 1990s included Bell Atlantic Infospeed, BellSouth FastAccess DSL, Charter Pipeline, GTE Internet Solutions, MediaOne Express, Optimum Online, Pacific Bell Internet, Road Runner, SBC DSL, and the @home network.
At this point, lack of availability prevented most people from using broadband services. In 1999, less than half of American homes had access to broadband technology, and fewer than 1 percent of American adults had broadband service in their home.
wireless
Wireless networks use radio waves to blanket an area with connectivity. To access the network, a device must have a wireless card and be within range of an access point. Internet connections may or may not be included, depending on the needs of the organization. The technology was introduced to businesses and colleges in 1991 and to the home market in 1999.
Depending on the number of access points, a wireless network can be as small as an office or as large as a city. Networks using radio towers can provide nationwide or even international coverage.
Some wireless networks were created solely to provide Internet access points for public use. These hotspots began to appear in hotels, airports and cafes in 1997. Long-distance coverage by radio tower was also launched that year. The term wi-fi was first used in 1999.
mobile
In 1993, some mobile devices could access e-mail by connecting to a paging service. Cell phone providers began to carry the Internet on their cellular networks in 1996. The first lightweight mobile web pages also appeared in 1996. You can read more about it at my Products & Technology page.
| |

The Sound Of Dial-Up Internet
|
_________________________________________
|
|
|
RetroLisa
| ________________________________________________________________________ | __ | ________________________ | _______ | Online Trends
internet use
Between 1990 and 1999, the number of Internet users in the United States increased from two million to 100 million. We reached a milestone in 1999, when Internet users outnumbered non-users for the first time.
The term "surfing the Internet" was first used in 1992. The term "information superhighway" also came into common usage in the 1990s. It originally referred to the interactive TV and phone network that scientists believed was just around the corner. This network never happened, but the Web did happen, and soon the term was applied to the Internet exclusively.
internet traffic
In 1990, before the Web existed, file downloading was the most popular activity on the Internet, followed by Telnet and e-mail. By 1995, the other activities had declined and the Web now accounted for 45 percent of Internet traffic. In 2000, the Web accounted for over half of all Internet traffic, followed by peer-to-peer file sharing, file downloading, e-mail, and video streaming.
web growth
As the Web increased in popularity, many traditional databases and services established websites to provide access to their content. The line between the Web and the Internet became increasingly blurred.
1991: 1 web server, 4 web pages. By the end of the year, there were 10 web servers.
1992: 50 websites on 26 web servers.
1993: At the beginning of the year, there were 130 websites on 50 servers. By the end of the year, there were 623 websites on 200 servers.
1994: 10,000 websites.
1995: 23,500 websites.
1996: 603,367 websites.
1997: 1 million websites.
1998: 4 million websites.
1999: 10 million websites.
web & internet issues
The late 1990s brought some new problems. They included viruses, fraudulent websites, and an increase in the amount of spam (junk e-mail). Copyright infringement issues came to the forefront, especially regarding the sharing of music. The presence of pornographic websites and online sexual predators gave parents cause for concern during this time, as well.
The Origin Of "Spam"
The First Commercial Spam
| |
|
_________________________________________
|
|
|
RetroLisa
| ___________________________________________________________________ | __ | _____________________________ | _______ | Popular Websites
search engines & web guides
Before there were search engines, there were web directories. Some of the first directories were Virtual Library, Global Network Navigator, and an early version of Yahoo. Directories display results in a menu format and require constant manual updating.
Search engines, on the other hand, use automated bots or spiders to regularly crawl the web. Sites are indexed by the bots and retrieved through the use of search terms. The technology was introduced in 1993. Popular early search engines included the World Wide Web Worm, WebCrawler, MetaCrawler, Infoseek, Lycos, Dogpile, Alta Vista, and HotBot. In the late 1990s, new search engines included Ask Jeeves, All The Web, Google, and Yahoo Search.
90s Search Engines Then & Now

web portals & homepages
Every web browser needs a starting point when it first opens. This website is known as a start page or homepage. After wandering around the Web, clicking on the "home" button will bring you back to your homepage. In the late 1990s, many sites competed for the opportunity to be a user's homepage and a doorway to the rest of the Web.
A web portal pulls content from diverse sources and combines it on a single site. Portals function well as homepages and act as hubs for news, entertainment, search engines and e-mail. Popular portals in the 1990s included Go, Excite, Yahoo, Netscape, Lycos, and the iVillage network for women. Several internet service providers also launched websites that functioned as web portals, including America Online and MSN Network. For children, the Kiddonet portal featured games, homework help, e-mail, free webpages, and a kid-friendly browser.
In 1998, Yahoo was the most-visited site on the Web.
The History Of Yahoo
government sites
In 1993, both the White House and the United Nations established websites. The first city websites went online in 1994. When tax time rolled around in 1995, the IRS established a website providing assistance and downloadable tax forms.
commerce
The Internet was originally a non-profit network sponsored by research organizations. Commercial enterprises were strictly prohibited. When this regulation was lifted in 1991, the Internet became a money-making venture for both entrepreneurs and investors. Many Internet-based businesses were launched between 1995 and 2001, creating what was known as the dot-com bubble. The bubble burst in 2001 when many of these businesses failed.
1994 gave us the first banner ads and the first cyberbank. New online shopping sites included Amazon (1995), eBay (1995), and Peapod (1996). PayPal was founded in 1998 to make paying for items on the Internet easier and more secure. The first $50 fee for registering a domain name was charged in 1995.
The Dot-Com Bubble
Peapod
webcams
In 1993, the first webcam was the Trojan Room Coffee Machine at the University of Cambridge. FogCam went online at San Francisco State University in 1994, and (as of 2014) is currently the oldest webcam still in operation.
personal sites
The first web hosts went online in the mid 1990s. These sites offer the average user a place to create free personal webpages. GeoCities was the most popular host, followed by Tripod, Angelfire, FreeServers, FortuneCity, Homestead, and Xoom. Many colleges also gave students space to create their own webpages, and some internet service providers offered free web space as well. It became popular for personal websites with similar content to be linked in web rings.
Some personal websites were maintained in the form of online journals, with entries listed in reverse chronological order. The term weblog was first applied to these journals in 1997. The shortened term blog was first used in 1999.
Web Ring
other sites
The sole purpose of many early websites was to discuss, review, and hand out awards to other sites. This was especially helpful for the droves of newbies who came to the Web every day and had no idea where to begin.
Many personal sites offered free clipart, MIDI songs, and WAV sound clips for download. Several fun sites created by web hobbyists also garnered attention. They included the Hamster Dance and the Dancing Baby.
Launched in 1996, Bolt was one of the first social networking sites on the Web. Here, teens could create pages, chat with other members, join clubs, and share photos and videos.
Websites Founded Before 1995
The Oldest Surviving Websites
Internet '96
10 Websites We Loved In The 90s
| |


|
_________________________________________
|
|
|
RetroLisa
| ___________________________________________________________________ | __ | _____________________________ | _______ | Media, File Sharing & Gaming
audio & video
Streaming technology delivers Internet media to your computer and allows it to play without waiting for it to be downloaded. The technology was introduced in 1993. The first traditional radio station to add a live stream was WXYC in North Carolina, which went online in 1994. RealPlayer introduced a streaming audio player in 1995 and an audio/video player in 1997. By the late 1990s, Internet radio stations were becoming quite common.
When the MP3 audio format was introduced in 1993, it quickly became the preferred format for sharing music online. Users shared files illegally in chat rooms and on centralized download servers. At this point, the practice wasn't very widespread and had yet to make an impact on the music industry.
The first websites to specialize in legal music downloads appeared in 1993. Some sites offered free music, while others offered it on a pay-per-download basis. At this point, most sites featured independent artists. Music sites in the 1990s included the Internet Underground Music Archive (IUMA), Cductive, MP3.com, CDBaby, Ritmoteca and eMusic.
peer-to-peer file sharing
Peer-to-peer software allows a user to download files directly from another user's computer. Files are transferred between hard drives without the use of chat rooms, e-mail or centralized servers.
In 1999, Napster was the first peer-to-peer program. It was designed to share MP3 music files, and was so popular that it caused a marked decrease in CD sales after just one month of operation. Several copyright infringement lawsuits were filed in 2000, and Napster was shut down in 2001. It returned in 2003 as a legal pay site with a new owner.
online gaming
The most popular form of online gaming in the 1990s was the multi-user dungeon, or MUD. Introduced in 1978, these games allowed players to use Telnet or a similar program to log into a remote computer, where they could choose a character and play an adventure game in real time with other users. Several online services and bulletin board systems also offered MUDs for their members.
The MUD concept was taken a step further in 1996 when the first massively multiplayer online role playing games (MMORPGs) went online. Unlike a MUD, players of a massive online game install the game on their own computers and subscribe to a special Internet site for online play. This makes it possible for thousands of users to play simultaneously. Popular MMORPGs in the 1990s included Meridian 59, The Realm, Ultima Online, The Palace and WorldsAway.
In 1998, a new method of online gaming was born when Sega Dreamcast became the first video game console to include a built-in modem and Internet support for online play.
How The Old Napster Worked
WXYC, The First Radio Station On The Web
All About MUDS
| |

RealPlayer
|
_________________________________________
|
|
|
RetroLisa
| ___________________________________________________________________ | __ | _____________________________ | _______ | Bringing People Together
The Internet's greatest strength lies in its ability to connect people.
e-mail
Electronic mail has been around since the 1960s, and was introduced in its modern form in 1971. In 1992, the ability to send attachments was added. In the 1980s, e-mail provided many people with their first taste of the online world, and through the years it has remained the most widely-used network application. In the 1990s, the introduction of web-based e-mail services like Hotmail made it more popular than ever. In 1996, the amount of e-mail being sent in the United States surpassed the amount of postal mail for the first time.
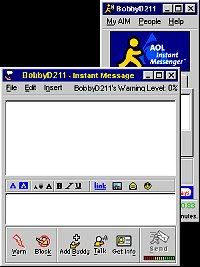
instant messaging
Instant messaging has also existed in various forms since the 1960s. In the 1980s, instant messaging programs were used by computer networks, online services and bulletin boards. The first widely-used messaging program was Internet Relay Chat, which was introduced in 1988. Other programs in use in the 1990s included PowWow, ICQ, AOL Instant Messenger, Jabber, Yahoo Pager and CU-SeeMe video chat.
chat rooms
Chat rooms can accommodate many users simultaneously. In the 1980s, CompuServe's CB Simulator was the ancestor of the modern chat room. Chat functions were also included in many multi-user games and bulletin board systems. In the 1990s, talkers were multi-user games with the game elements removed, leaving only the chat feature. They were the first real Internet chat rooms.
Specialized chat software and web-based chat rooms became popular in the 1990s. Although Internet Relay Chat was capable of sending instant messages, it was used primarily for group conversations, and was particularly useful during the Gulf War. In the late 1990s, ParaChat was the most popular provider of web-based chat rooms and networks. America Online also provided chat rooms for its members.
forums & newsgroups
In the late 1990s, the Web forced thousands of bulletin board systems to either embrace the new technology or compete with it. Many boards did both....they remained off the Web and provided access to their content through support websites. Most boards, however, chose to shut down. To replace them, new web-based message boards were created.
Usenet began hosting its archived threads on the Web in 1995. The first web-based Usenet servers appeared in the late 1990s.
e-cards
A very popular activity in the 1990s was sending online greeting cards, or e-cards. The first website specializing in e-cards was launched in 1994. In the late 1990s, Blue Mountain Arts was the most popular provider of virtual cards.
| |

List Of Emoticons
Talker History
Chat Abbreviations
Blue Mountain E-Cards
Internet Relay Chat
AOL Instant Messenger
|
_________________________________________
|
|
|
